A coreless induction furnace is an advanced metal melting solution that operates without an iron core inside the coil. By utilizing electromagnetic induction, it rapidly heats metals with high efficiency, precision, and environmental friendliness. Among coreless furnaces, power-frequency and medium-frequency types are most widely used across industrial sectors. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of coreless induction furnaces, covering structure, operation, benefits, applications, and common challenges, helping global buyers make informed decisions.
Structure of a Coreless Induction Furnace
A modern coreless induction furnace consists of several critical components designed for efficiency, safety, and durability:
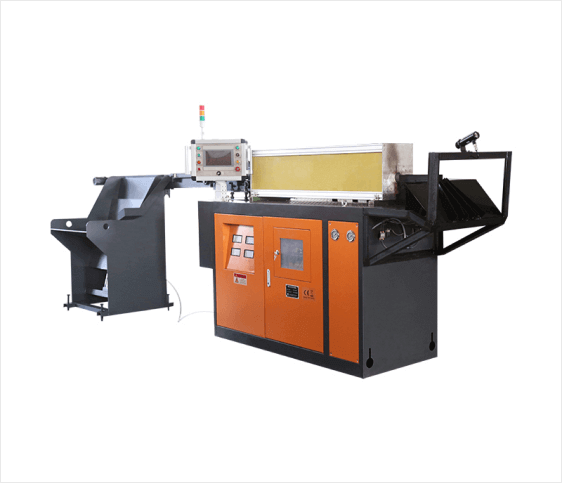
1. Furnace Body
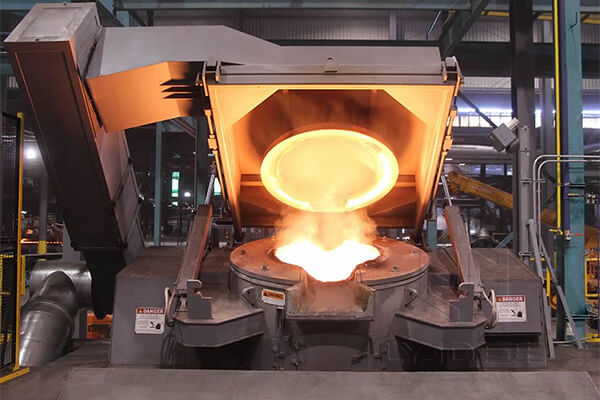
The furnace body is the main chamber, typically made of high-quality refractory materials in round or square crucibles. The hollow interior holds the metal charge for melting. Observation windows at the top allow operators to safely monitor and add materials.
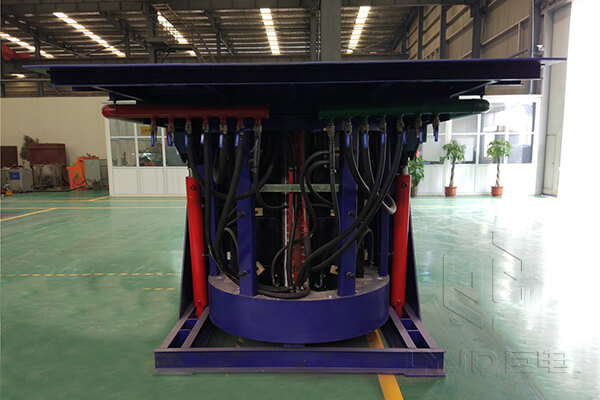
2. Furnace Frame
The furnace frame supports the furnace body, usually constructed from welded steel plates and section steel. Most furnaces include a tilting mechanism for easy and controlled pouring of molten metal.
3. Auxiliary Devices
- Tilting Devices: Can be manual, hydraulic, or motor-driven for smooth metal discharge.
- Dust Collection & Exhaust Systems: Ensure a cleaner, safer work environment by removing smoke and dust.
4. Cooling System
- Water Cooling: Protects the induction coil and furnace shell from overheating.
- Air Cooling: Regulates the temperature of cooling water, maintaining stable operation.
5. Power Supply & Control System
Key components include transformers, rectifiers, reactors, and control cabinets:
- Transformers adjust voltage for the coil.
- Rectifiers convert AC to DC as needed.
- Reactors stabilize current and reduce fluctuations.
- Control cabinets manage the overall operation, temperature, and safety interlocks.
How Coreless Induction Furnaces Work
Coreless induction furnaces operate on electromagnetic induction principles. When AC passes through the coil:
- Eddy Currents form in the metal, generating heat.
- The heat rapidly raises the metal surface temperature.
- Continuous induction melts the metal into liquid form efficiently.
This non-contact heating method ensures uniform melting, precise temperature control, and minimal energy loss. Unlike cored induction furnaces, coreless designs avoid magnetic saturation issues, extending coil lifespan.
Key Advantages
1. Simplified Structure & Easy Maintenance
Fewer components reduce manufacturing complexity and maintenance costs. Operators find it easier to control and maintain.
2. Fast Heating & High Efficiency
Metals reach target temperatures quickly, improving production speed and throughput.
3. Energy Saving & Eco-Friendly
Shorter melting cycles lower electricity consumption and reduce emissions.
4. Operational Flexibility
Coreless furnaces can start or stop as needed, accommodating variable production demands.
5. Low Lining Costs & Long Service Life
Standard refractory materials suffice, lowering maintenance costs. Coils last longer since they are not affected by core saturation.
6. Clean & Safe Process
No combustion, smoke, or pollution occurs, making it safer for workers and the environment.
Applications of Coreless Induction Furnaces
Coreless induction furnaces are versatile and widely applied:
- Steel Industry: Heating billets, insulating molten iron, and alloy processing.
- Non-Ferrous Metals: Aluminum melting, copper smelting, and alloy manufacturing.
- Automotive Industry: Efficiently producing high-quality components while reducing costs.
- Residential/Commercial Applications: Advanced kitchen induction stoves or energy-efficient home heating systems.
By providing precise temperature control, high thermal efficiency, and flexibility, these furnaces enhance productivity and ensure superior metal quality.
Common Operational Challenges
Even with advanced technology, some challenges may occur:
- Furnace Lining Erosion: Caused by mechanical wear, molten metal flow, or chemical reactions.
- Metal Leakage: Occurs if lining density is insufficient or sintering is incomplete.
- Lining Slagging: Oxides or impurities can stick to the furnace wall, reducing efficiency.
- Spalling & Cracks: Thermal stress, mechanical impact, or uneven expansion can damage refractory materials.
Proper maintenance, careful material selection, and monitoring reduce risks and extend furnace life.
Conclusion
A coreless induction furnace is a reliable, high-efficiency, and environmentally friendly metal melting solution. It combines fast heating, operational flexibility, low energy consumption, and clean processing. For industrial buyers seeking to optimize productivity, reduce costs, and maintain high-quality output, investing in a coreless induction furnace is a smart, long-term decision.
Discover how a coreless induction furnace can transform your production process—enhance efficiency, save energy, and improve product quality today.