A steel casting line, also called a steel foundry production line, is a specialized manufacturing system designed to produce durable and complex steel parts. Unlike machining or forging, steel casting allows companies to create large, intricate, or custom components in a cost-effective way. Because of these advantages, steel castings play a crucial role in industries such as automotive, construction, mining, and energy.
To better understand how it works, let’s walk through the main stages of a modern steel casting line.
1. Pattern and Mold Design
Every casting project starts with a pattern—a replica of the final product. Engineers design this pattern from wood, plastic, or metal depending on the precision required. They also attach a gating system that directs molten steel into the mold cavity. With a well-prepared pattern, foundries can reduce defects and improve flow efficiency.
2. Mold Making
Next, technicians create the mold. They pack sand or refractory material around the pattern to form a cavity. Because molten steel reaches extremely high temperatures, the mold material must stay strong and stable. By selecting the right material, the foundry ensures that the mold holds its shape until the steel solidifies.
3. Melting and Alloying
After preparing the molds, workers melt raw steel in induction or arc furnaces. They can also add alloying elements—such as chromium, nickel, or molybdenum—to adjust hardness, toughness, or corrosion resistance. Careful melting and alloying allow the foundry to deliver castings with properties that match customer requirements.
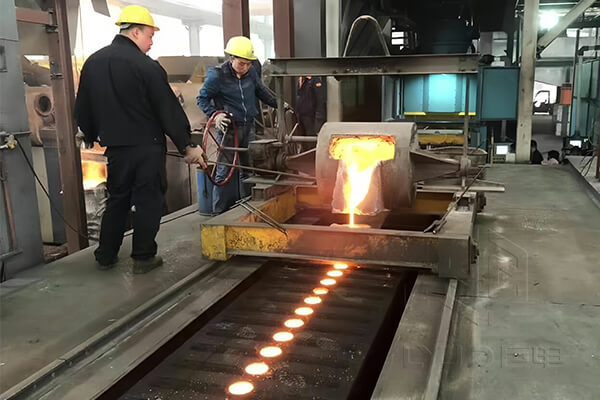
4. Pouring and Solidification
Once the steel reaches the right temperature, operators pour it into the molds. As the metal fills the cavity, it begins to cool and solidify. Because cooling affects quality, foundries monitor the process closely. Controlled solidification reduces cracks, porosity, and uneven grain structures.
5. Shakeout and Cleaning
After solidification, workers remove the mold in a step called shakeout. They then clean the raw castings to eliminate sand, slag, or excess material. Methods like shot blasting, grinding, or chemical treatment give the casting a smoother finish and prepare it for further processing.
6. Finishing Processes
At this stage, the castings move through additional treatments:
- Machining improves precision and dimensional accuracy.
- Heat treatment strengthens the steel and enhances durability.
- Surface coating or painting protects against corrosion and wear.
These finishing steps transform raw castings into ready-to-use components.
7. Quality Control and Testing
Quality assurance runs through every stage of production. Foundries apply non-destructive testing methods such as:
- Ultrasonic inspection for internal cracks
- X-ray imaging for structural consistency
- Dye or magnetic particle testing for surface flaws
With these inspections, manufacturers guarantee that each casting meets international standards (ISO, ASTM, EN), giving global buyers full confidence.
8. Packaging and Shipping
Finally, workers package the finished castings securely and prepare them for delivery. Whether stored in warehouses or shipped overseas, careful handling ensures that customers receive castings on time and in excellent condition.
Why Steel Casting Lines Matter
- Flexibility: Produce complex shapes that other methods cannot achieve.
- Strength: Handle heavy loads in demanding environments.
- Efficiency: Save costs by reducing material waste and machining work.
- Versatility: Supply critical parts for automotive, mining, construction, and energy sectors.
Conclusion
A steel casting line is not just a production system—it is a complete solution for global industries. By combining advanced melting technology, precise mold design, and strict quality control, suppliers can deliver steel castings that meet the highest standards.
For international buyers, choosing a manufacturer with a modern steel casting line means better quality, faster delivery, and lower risk. As industries continue to demand stronger and more complex parts, steel casting remains one of the most reliable and future-ready manufacturing processes in the world.